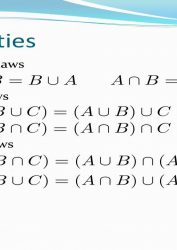Definitions: Universal set : I Empty set: ∅ Union of sets A∪B={x:x∈A or x∈B} Intersection of sets A∩B={x:x∈A and x∈B} Complement A′={x∈I:x∉A} Difference of sets A∖B={x:x∈A and x∉B} Cartesian product A×B={(x,y):x∈A and y∈B} Set identities involving union Commutativity A∪B=B∪A Associativity A∪(B∪C)=(A∪B)∪C Idempotency A∪A=A Set identities involving intersection Commutativity A∩B=B∩A Associativity A∩(B∩C)=(A∩B)∩C Idempotency A∩A=A Set identities involving union and intersection Distributivity A∪(B∩C)=(A∪B)∩(A∪C) A∩(B∪C)=(A∩B)∪(A∩C) Domination A∩∅=∅ A∪I=I Identity A∪∅=∅ A∩I=A Set identities involving union, intersection and complement Complement of intersection and union A∪A′=I A∩A′=∅ De Morgan’s laws (A∪B)′=A′∩B ′ (A∩B)′=A′∪B ′ Set identities involving difference B∖A=B∖(A∪B) B∖A=B∩A′ A∖A=∅ (A∖B)∩C=(A∩C)∖(B∩C) A′=I∖A
Category: Algebra Formulas
Mathematics Articles
Current Density Formula
In the field of electromagnetism, Current Density is the measurement of electric current (charge flow in amperes) per unit area of cross-section (m2). This is a vector quantity, with both a magnitude (scalar) and a direction. J = I/A J = current density in amperes/m2 I = current through a conductor, in amperes A = cross-sectional area of the conductor, m2 Current Density Formula Questions: 1) A current of 6 mA is flowing through a copper wire that has an area of 4 mm2. What is the current density? Answer: The…
Here is a list of Algebraic formulas
Algebraic formulas a2 – b2 = (a – b)(a + b) (a+b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 a2 + b2 = (a – b)2 + 2ab (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2 (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2ac + 2bc (a – b – c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 – 2ab – 2ac + 2bc (a + b)3 = a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + b3 ; (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b) (a – b)3 = a3 – 3a2b + 3ab2 – b3 a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + ab + b2) a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 –…
Algebra Formulas
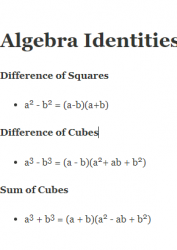
Algebra Identities Difference of Squares a2 – b2 = (a-b)(a+b) Difference of Cubes a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2+ ab + b2) Sum of Cubes a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 – ab + b2) Special Algebra Expansions Formula for (a+b)2 and (a-b)2 (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab +b2 Formula for (a+b)3 and (a-b)3 (a + b)3 = a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + b3 (a – b)3 = a3 – 3a2b + 3ab2 – b3 Roots of Quadratic Equation Formula Consider this quadratic equation: ax2 + bx + c = 0 Where a, b and c are the leading coefficients. The…